NFIP Foundations: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| (43 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{info-nfip-sfip}} | |||
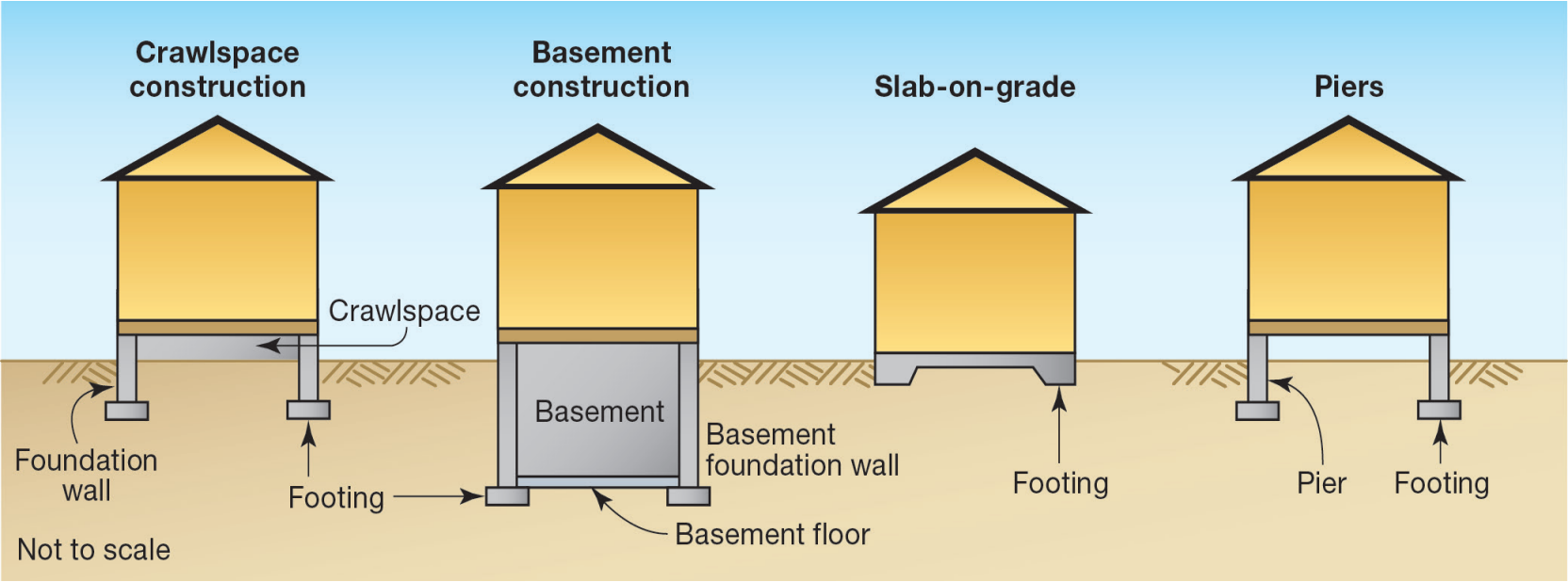
The NFIP classifies buildings based on their foundation type, which plays a critical role in determining flood risk, rating, and eligibility for coverage. The two mutually exclusive foundation classifications are '''elevated buildings''' and '''non-elevated buildings'''. | |||
The NFIP classifies buildings based on their foundation type, which plays a critical role in determining flood risk, rating, and eligibility for coverage. The two mutually exclusive foundation classifications are '''elevated buildings''' and '''non-elevated buildings'''. | |||
NFIP Foundations are similar to [[Building Diagram Numbers]]. | |||
{{img-proc-nofrm | |||
|file = File:Img-nfip-foundations-01.png | |||
}} | |||
{{box-summ | |||
|title = Important! | |||
|color = orange | |||
|text = | |||
Choosing the '''correct foundation is essential''' for completing the NFIP application and ensuring proper coverage. | |||
Incorrectly identifying a foundation can lead to '''improper rating or coverage issues''', potentially affecting '''claims processing'''. | |||
}} | |||
== Non-Elevated Buildings == | == Non-Elevated Buildings == | ||
A '''non-elevated building''' is constructed on a foundation where the lowest floor is at or below ground level on all sides. Find more details in the {{FIM|page=75}}. | |||
Common foundation types for non-elevated buildings include: | |||
* Slab-on-grade | |||
* Basement | |||
* Crawlspace with the lowest floor below grade on all sides | |||
These buildings are generally more susceptible to flood damage and may face higher premiums due to increased risk. | |||
=== Below Ground versus Below Grade === | |||
Unless it meets [[NFIP Coverage Exceptions#Buildings Below Ground|specific requirements]], a building constructed below ground is ineligible for coverage. '''Below Ground''' is defined as more than 49% of the building's Actual Cash Value (ACV) sits at or below the surrounding grade. [https://www.fema.gov/sites/default/files/documents/fema_nfip_flood-insurance-manual_042024.pdf#page=192] | |||
A building constructed '''below grade''' is eligible for coverage, so long as the majority of the building is above grade. Below grade (also known as "subgrade" or "sub-grade") foundations are classified as non-elevated. | |||
== Elevated Buildings == | == Elevated Buildings == | ||
An '''elevated building''' is constructed with the lowest floor above ground level, supported by a foundation that provides open space beneath the structure. Find more details in the {{FIM|page=77}}. | |||
Examples of elevated foundations include: | |||
* Piers or pilings | |||
* Posts or columns | |||
* Enclosed areas used solely for parking, storage, or building access | |||
Elevated buildings are designed to minimize flood damage by reducing the risk of floodwaters reaching the primary living areas. They typically qualify for lower premiums because of their reduced risk profile. | |||
Elevated buildings can also have [[#Enclosures|enclosures]]. | |||
The NFIP uses six foundation types to assess building structures for flood insurance purposes. These types influence policy ratings, flood mitigation requirements, and overall risk assessment. Accurate classification of foundation types ensures proper flood insurance rating and compliance with NFIP regulations. | |||
Agents should use all available documentation, including [[Elevation Certificates]] and photographs, to verify foundation details. | |||
'''[[Equinox]]''' displays foundation images during the [[Create NFIP Application|application process]]. | |||
== Foundation Types == | |||
=== 1. Slab === | |||
* '''Description''': A concrete slab poured directly on the ground. | |||
* '''Key Features''': | |||
** No airspace between the ground and the first floor. | |||
** Common in areas with minimal flood risk. | |||
* '''Classification''': Non-Elevated. | |||
* '''[[Building Diagram Numbers]]''': 1A, 1B, 3 | |||
* {{FIM|page=75}} | |||
=== 2. Basement === | |||
* '''Description''': A space where the floor is below ground level (subgrade) on all sides. | |||
* '''Key Features''': | |||
** Includes structures like sunken rooms or subgrade crawlspaces deeper than 2 feet below the Lowest Adjacent Grade (LAG). | |||
** High flood risk due to water intrusion potential. | |||
* '''Classification''': Non-Elevated. | |||
* '''[[Building Diagram Numbers]]''': 2A, 2B, 4 | |||
* {{FIM|page=76}} | |||
=== 3. Elevated on Posts, Piles, or Piers Without Enclosure === | |||
* '''Description''': A building raised above ground on posts, piles, piers, or similar supports with no enclosure underneath. | |||
* '''Key Features''': | |||
** Allows unobstructed flow of floodwaters. | |||
** Common in coastal and high-velocity flood zones. | |||
* '''Classification''': Elevated. | |||
* '''[[Building Diagram Numbers]]''': 5 | |||
* {{FIM|page=77}} | |||
=== 4. Elevated on Posts, Piles, or Piers With Enclosure === | |||
* '''Description''': Similar to the above type but includes an enclosed area beneath the elevated structure. | |||
* '''Key Features''': | |||
** Requires proper venting to allow floodwaters to pass through and reduce structural damage. | |||
** Enclosures are typically limited to storage or parking. | |||
* '''Classification''': Elevated. | |||
* '''[[Building Diagram Numbers]]''': 6 | |||
* {{FIM|page=79}} | |||
=== 5. Elevated on Solid Foundation Walls With Enclosure === | |||
* '''Description''': A building elevated on solid perimeter foundation walls with an enclosed area beneath. | |||
* '''Key Features''': | |||
** Requires venting and flood-resistant materials in the enclosure to comply with NFIP standards. | |||
** Used in areas with moderate flood risk. | |||
* '''Classification''': Elevated. | |||
* '''[[Building Diagram Numbers]]''': 7 | |||
* {{FIM|page=79}} | |||
=== 6. Crawlspace === | |||
* '''Description''': A shallow area between the ground and the first floor, typically used for utilities. | |||
* '''Key Features''': | |||
** Crawlspaces can be '''above-grade''' (elevated) or '''subgrade''' (non-elevated). | |||
** Subgrade crawlspaces require specific elevation and venting to avoid classification as basements. | |||
* '''Classification''': Can be Elevated or Non-Elevated depending on its relation to the LAG. | |||
* '''[[Building Diagram Numbers]]''': 8, 9 | |||
* {{FIM|page=80}} | |||
== Enclosures == | |||
An NFIP Enclosure is any area of an elevated building that is enclosed by walls on all sides and located below the elevated floor. Enclosures are used only for parking, building access, or storage. | |||
An enclosure's size (area or square footage) does not have to match the footprint of the building. | |||
* If it does, the enclosure is called a "full enclosure" or "fully enclosed". | |||
* If it does not, the enclosure is called a "partial enclosure" or "partially enclosed". | |||
The full definition can be found in the {{FIM|page=78}}. | |||
== Walkout Basements == | |||
Walkout basements are elevated buildings, while sub-grade basements are non-elevated and subject to higher flood risks. The critical difference lies in '''ground slope''' and whether any walls are fully above grade. | |||
=== Walkout Basement vs. Sub-Grade Basement: A Quick Comparison === | |||
{| class="wikitable" | |||
!'''Feature''' | |||
!'''Walkout Basement''' | |||
!'''Sub-Grade Basement''' | |||
|- | |||
|'''Definition''' | |||
|A basement with at least one wall fully above grade, providing direct access to the outside. | |||
|A basement with the floor below ground level (subgrade) on all sides. | |||
|- | |||
|'''Building Diagram''' | |||
|Diagram 7 (Elevated Building). | |||
|Diagram 2 (Non-Elevated Building). | |||
|- | |||
|'''Ground Characteristics''' | |||
|Built on sloping ground, with higher grade accessible from the upper floor. | |||
|Built on flat or near-flat ground, fully surrounded by subgrade walls. | |||
|- | |||
|'''Flood Risk''' | |||
|Reduced flood risk due to elevation; venting may still be required. | |||
|Higher flood risk; prone to water intrusion from all sides. | |||
|- | |||
|'''NFIP Classification''' | |||
|Considered an '''elevated building'''. | |||
|Considered a '''non-elevated building'''. | |||
|- | |||
|'''Common Misunderstanding''' | |||
|Often mistaken for a traditional basement due to its name. | |||
|Clear classification as subgrade on all sides. | |||
|} | |||
{{nfip}} | |||
Latest revision as of 07:44, 26 March 2025
The NFIP classifies buildings based on their foundation type, which plays a critical role in determining flood risk, rating, and eligibility for coverage. The two mutually exclusive foundation classifications are elevated buildings and non-elevated buildings.
NFIP Foundations are similar to Building Diagram Numbers.
| Important! |
Choosing the correct foundation is essential for completing the NFIP application and ensuring proper coverage.
Incorrectly identifying a foundation can lead to improper rating or coverage issues, potentially affecting claims processing.
|
Non-Elevated Buildings
A non-elevated building is constructed on a foundation where the lowest floor is at or below ground level on all sides. Find more details in the FIM.
Common foundation types for non-elevated buildings include:
- Slab-on-grade
- Basement
- Crawlspace with the lowest floor below grade on all sides
These buildings are generally more susceptible to flood damage and may face higher premiums due to increased risk.
Below Ground versus Below Grade
Unless it meets specific requirements, a building constructed below ground is ineligible for coverage. Below Ground is defined as more than 49% of the building's Actual Cash Value (ACV) sits at or below the surrounding grade. [1]
A building constructed below grade is eligible for coverage, so long as the majority of the building is above grade. Below grade (also known as "subgrade" or "sub-grade") foundations are classified as non-elevated.
Elevated Buildings
An elevated building is constructed with the lowest floor above ground level, supported by a foundation that provides open space beneath the structure. Find more details in the FIM.
Examples of elevated foundations include:
- Piers or pilings
- Posts or columns
- Enclosed areas used solely for parking, storage, or building access
Elevated buildings are designed to minimize flood damage by reducing the risk of floodwaters reaching the primary living areas. They typically qualify for lower premiums because of their reduced risk profile.
Elevated buildings can also have enclosures.
The NFIP uses six foundation types to assess building structures for flood insurance purposes. These types influence policy ratings, flood mitigation requirements, and overall risk assessment. Accurate classification of foundation types ensures proper flood insurance rating and compliance with NFIP regulations.
Agents should use all available documentation, including Elevation Certificates and photographs, to verify foundation details.
Equinox displays foundation images during the application process.
Foundation Types
1. Slab
- Description: A concrete slab poured directly on the ground.
- Key Features:
- No airspace between the ground and the first floor.
- Common in areas with minimal flood risk.
- Classification: Non-Elevated.
- Building Diagram Numbers: 1A, 1B, 3
- FIM
2. Basement
- Description: A space where the floor is below ground level (subgrade) on all sides.
- Key Features:
- Includes structures like sunken rooms or subgrade crawlspaces deeper than 2 feet below the Lowest Adjacent Grade (LAG).
- High flood risk due to water intrusion potential.
- Classification: Non-Elevated.
- Building Diagram Numbers: 2A, 2B, 4
- FIM
3. Elevated on Posts, Piles, or Piers Without Enclosure
- Description: A building raised above ground on posts, piles, piers, or similar supports with no enclosure underneath.
- Key Features:
- Allows unobstructed flow of floodwaters.
- Common in coastal and high-velocity flood zones.
- Classification: Elevated.
- Building Diagram Numbers: 5
- FIM
4. Elevated on Posts, Piles, or Piers With Enclosure
- Description: Similar to the above type but includes an enclosed area beneath the elevated structure.
- Key Features:
- Requires proper venting to allow floodwaters to pass through and reduce structural damage.
- Enclosures are typically limited to storage or parking.
- Classification: Elevated.
- Building Diagram Numbers: 6
- FIM
5. Elevated on Solid Foundation Walls With Enclosure
- Description: A building elevated on solid perimeter foundation walls with an enclosed area beneath.
- Key Features:
- Requires venting and flood-resistant materials in the enclosure to comply with NFIP standards.
- Used in areas with moderate flood risk.
- Classification: Elevated.
- Building Diagram Numbers: 7
- FIM
6. Crawlspace
- Description: A shallow area between the ground and the first floor, typically used for utilities.
- Key Features:
- Crawlspaces can be above-grade (elevated) or subgrade (non-elevated).
- Subgrade crawlspaces require specific elevation and venting to avoid classification as basements.
- Classification: Can be Elevated or Non-Elevated depending on its relation to the LAG.
- Building Diagram Numbers: 8, 9
- FIM
Enclosures
An NFIP Enclosure is any area of an elevated building that is enclosed by walls on all sides and located below the elevated floor. Enclosures are used only for parking, building access, or storage.
An enclosure's size (area or square footage) does not have to match the footprint of the building.
- If it does, the enclosure is called a "full enclosure" or "fully enclosed".
- If it does not, the enclosure is called a "partial enclosure" or "partially enclosed".
The full definition can be found in the FIM.
Walkout Basements
Walkout basements are elevated buildings, while sub-grade basements are non-elevated and subject to higher flood risks. The critical difference lies in ground slope and whether any walls are fully above grade.
Walkout Basement vs. Sub-Grade Basement: A Quick Comparison
| Feature | Walkout Basement | Sub-Grade Basement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A basement with at least one wall fully above grade, providing direct access to the outside. | A basement with the floor below ground level (subgrade) on all sides. |
| Building Diagram | Diagram 7 (Elevated Building). | Diagram 2 (Non-Elevated Building). |
| Ground Characteristics | Built on sloping ground, with higher grade accessible from the upper floor. | Built on flat or near-flat ground, fully surrounded by subgrade walls. |
| Flood Risk | Reduced flood risk due to elevation; venting may still be required. | Higher flood risk; prone to water intrusion from all sides. |
| NFIP Classification | Considered an elevated building. | Considered a non-elevated building. |
| Common Misunderstanding | Often mistaken for a traditional basement due to its name. | Clear classification as subgrade on all sides. |