First Floor Height
First Floor Height (FFH) is a measurement used to determine the elevation of a building's lowest floor above the adjacent ground level. This measurement plays a critical role in flood insurance rating by helping assess the building's flood risk accurately.
How to Measure FFH
First Floor Height is determined based on the building's foundation type. The table below outlines common foundation types and how FFH is measured. The measurement will be to the Lowest Adjacent Grade (LAG), or the lowest point where the surrounding ground touches the foundation.
| Foundation | Where to Measure | Image |
|---|---|---|
| Slab on Grade | From the LAG to the top of the slab floor | 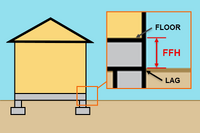
|
| Basement | From the LAG to the first floor above the basement | 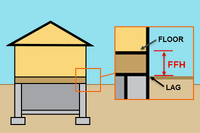
|
| Elevated without Enclosure | From the LAG to the top of the lowest elevated floor | 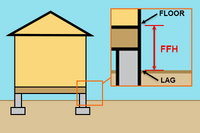
|
| Post-FIRM Elevated with Enclosure | From the LAG to the top of the lowest elevated floor
Only applies to Post-FIRM buildings in zones A1-A30, AE, AH, AR, AR/A, AR/AE, AR/AH, AR/A1-A30, V1-V30, or VE. |
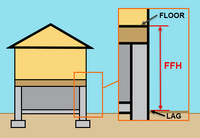
|
| Pre-FIRM Elevated with Enclosure | From the LAG to the top of the enclosure floor
Applies to
|
|
| Crawlspaces | From the LAG to the top of the lowest elevated floor | 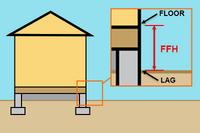
|
FEMA uses advanced datasets to calculate FFH if no Elevation Certificate is provided.
Why Does FFH Matter?
- Risk Assessment: FFH is a key factor in calculating flood insurance premiums. A higher FFH generally reduces flood risk and may lead to lower premiums.
- Flexible Options for Policyholders: FEMA provides an FFH value, but policyholders can also submit an Elevation Certificate (EC) from a licensed surveyor, which may result in a lower premium.
Additional Notes for Agents
- Submitting an Elevation Certificate won't increase the premium and might result in a lower cost for the policyholder.
- Ensure the FFH and supporting documentation are accurately recorded on the insurance application form to avoid processing delays.
For more detailed guidance, consult the FIM.